Consider now a frame ![]() [ i.e. a set of spatial coordinates
(x,y,z) and a time coordinate t ], and another frame
[ i.e. a set of spatial coordinates
(x,y,z) and a time coordinate t ], and another frame ![]() with coordinates
with coordinates ![]() which moves in
the x direction with uniform speed v relative to the frame
which moves in
the x direction with uniform speed v relative to the frame ![]() .
.
Common sense suggests that the two sets of coordinates are related by
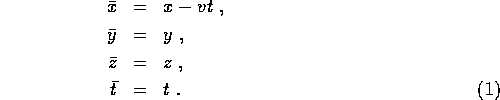
These are the Galelian transformations .

If the particle has a velocity ![]() with components
with components
![]() in
in ![]() , its velocity in
, its velocity in ![]() is:
is:
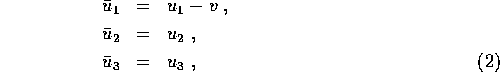
or
![]()
where
![]()
More generally if the coordinate axes and the origins of ![]() and
and ![]() differ then:
differ then:
![]()
where ![]() has components (x,y,z). Here
has components (x,y,z). Here ![]() is a
rotation matrix aligning
is a
rotation matrix aligning ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() is
the relative velocity of
is
the relative velocity of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() and
and
![]() is the displacement of the origin from
is the displacement of the origin from ![]() .
.
Since the transformation is linear [ constant velocity
in ![]()
![]() constant velocity in
constant velocity in ![]() ],
], ![]() is inertial if
is inertial if ![]() is.
is.
Thus there are an infinite set of inertial frames, all moving uniformly with respect to each other.
All of Newtons laws apply in any inertial frame since
![]()
and ![]() is invariant. Thus we have Newtonian
[ Galelian ] Relativity.
is invariant. Thus we have Newtonian
[ Galelian ] Relativity.
The laws of mechanics do not allow measurement of absolute velocity, however one can measure absolute acceleration.
Newton explained inertial frames in terms of absolute space identified with the center of mass of the solar system or a frame of ``fixed stars''. However this is unsatisfactory because: